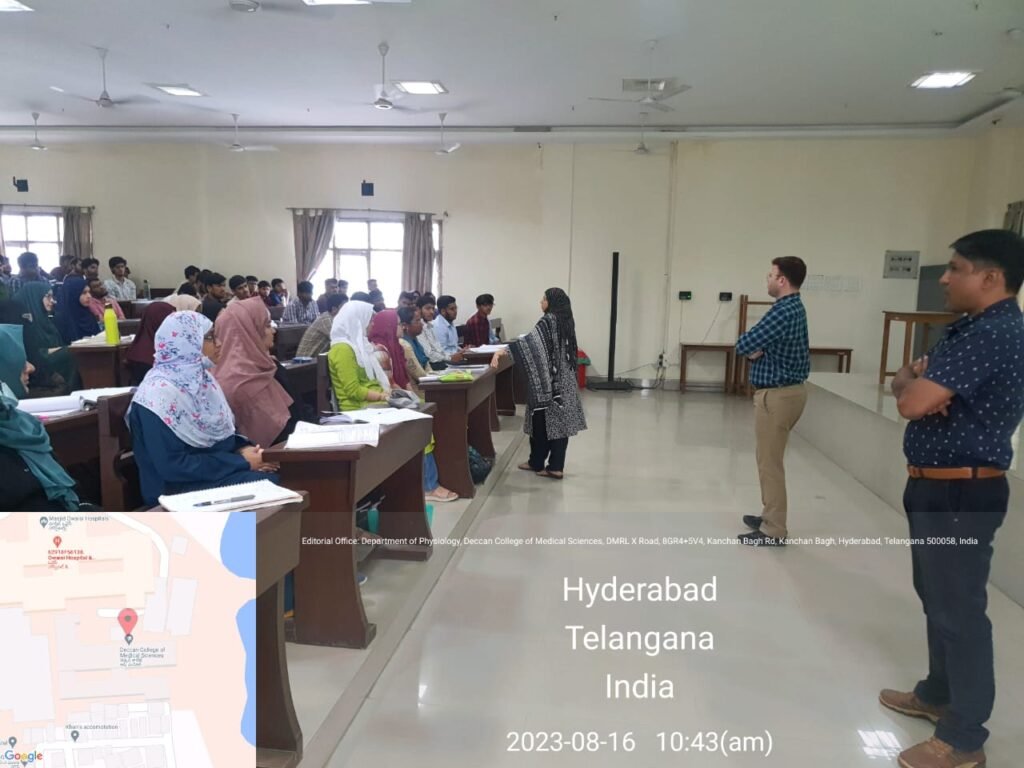
NMC / University
- Home
- NMC / University
Aadhar Enabled Biometric Attendance System (AEBAS) attendance dashboard of Deccan College of Medical Sciences faculty.
Visit the link: https://dcmshyd.nmcindia.ac.in/
Information under Clause (NMC) A.1.16 and under Clause (MCI) B1.11 of Minimum Standard Requirement Regulations, 1999
a) Details of Dean / Principal and Medical Superintendent Including their name, qualification, complete address with telephone and STD code, fax and E-mail, etc. (Updated 10-08-2023)

Dr. Ashfaq Hasan
Designation: Principal & Professor of Pulmonary Medicine
Qualification: MBBS, MD (Pulmonary Medicine)
Address: Deccan College of Medical Sciences, DMRL 'X' Road, Kanchanbagh, Hyderabad-500058, Telangana, India.
Phone: +91-40-24340225
Fax: +91-40-24340235
Email: principal@dcms.ac.in

Dr. Mohammed Abdul Majid Adil
Designation: Vice-Principal; Professor & HOD, Urology
Qualification: MBBS, MS, MCh (Urology)
Address: Deccan College of Medical Sciences, DMRL 'X' Road, Kanchanbagh, Hyderabad-500058, Telangana, India.
Phone: +91-40-24340225
Fax: +91-40-24340235
Email: vp@dcms.ac.in

Dr. Chavva Sham Sunder
Designation: Medical Superintendent (OHRC) , Professor of Orthopedics
Qualification: M.B.B.S., D.Ortho., M.S - Orthopaedics
Address: Owaisi Hospital & Research Center, DMRL 'X' Road, Kanchanbagh, Hyderabad-500058, Telangana, India.
Phone: +91-40-24343129
Fax: +91-40-24342596
Email: ms@owaisihospital.com

Dr. M. Aleemuddin Naveed
Designation: Medical Superintendent (PEH) & Professor of Pulmonary Medicine
Qualification: MBBS, MD (Respiratory Medicine)
Address: Princess Esra Hospital, Shah Ali Banda, Charminar, Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
Phone: +91-40-24343129
Fax: +91-40-24342596
Email: ms@princessesrahospital.com
b) Teaching Staff (Updated till 31-01-2026)
- Anatomy
- Biochemistry
- Physiology
- Pathology
- Pharmacology
- Microbiology
- Forensic Medicine
- Community Medicine
- Ophthalmology
- Otorhinolaryngology
- General Medicine
- General Surgery
- Orthopedics
- Obstetrics and Gynecology
- Pediatrics
- Anesthesiology
- Dermatology
- Dentistry
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonary Medicine
- Radiodiagnosis
- Radiation Oncology
- Emergency Medicine
- Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation
- Cardiology
- Cardiothoracic Vascular Surgery
- Neurology
- Gastroenterology
- Nephrology
- Urology
- Plastic Surgery
- Neurosurgery
- Endocrinology
- Anatomy
- Biochemistry
- Physiology
- Patghology
- Pharmacology
- Microbiology
- Forensic Medicine
- Community Medicine
- Ophthalmology
- Otorhinolaryngology
- General Medicine
- General Surgery
- Orthopedics
- Obstetrics and Gynecology
- Pediatrics
- Anesthesiology
- Dermatology
- Dentistry
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonary Medicine
- Radiodiagnosis
- Emergency Medicine
- Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation
- Cardiology
- Neurology
- Gastroenterology
- Nephrology
- Urology
- Plastic Surgery
- Neurosurgery
c) Details of the sanctioned intake capacity of various courses UG as well as PGs by the MCI/NMC/KNRUHS (Updated 26-07-2024)
d) List of students admitted merit-wise category-wise (UG & PG) for the current and previous year (Updated 26-07-2024)
e) Any research publications during the last one year (Updated 17-06-2025)
2025
Manorenj, Sandhya
Seizure Semiology in Clinical Practice: From symptom analysis to localization Book
Kindle, Amazon KDP, 2025, ISBN: 9798241833440.
@book{Manorenj_2025j,
title = {Seizure Semiology in Clinical Practice: From symptom analysis to localization},
author = {Sandhya Manorenj},
url = {https://www.amazon.in/Seizure-Semiology-Clinical-Practice-Localization-ebook/dp/B0GDHS7TFY},
isbn = {9798241833440},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-12-31},
number = { ASIN: B0GDHS7TFY },
publisher = {Amazon KDP},
edition = {Kindle},
abstract = {Seizure Semiology in Clinical Practice is designed as a practical and clinically oriented guide to understanding seizure manifestations and their localizing and lateralizing value. The book serves as a valuable resource for neurology residents, general medicine residents, epilepsy fellows, budding neurologists, epileptologists, and neurotechnologists by translating bedside observations into meaningful diagnostic insights. Emphasis is placed on real-world application, helping readers correlate seizure behaviors with underlying neuroanatomy and an approach to history taking. By strengthening clinical acumen and improving seizure recognition, this book ultimately supports accurate diagnosis, timely referral, and optimal management, thereby enhancing the quality of care delivered to patients with epilepsy and related seizure disorders.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {book}
}
Ali, Shireen Adeeb Mujtaba; Begum, Safia; Naveed, Mohammed Aleemuddin; Mujahid, Mohammed Naseeruddin
Precision Healthcare: Advancing Patient Care Through Decision Tools, Wearables, and Ethical Considerations Book Chapter
In: Gupta, Neeraj; Ibrahim, Abdelhameed; Vyas, Bhavesh; Jeet, Shobhna (Ed.): Precision Healthcare: Patient Care, Decision Tools, Wearables, Legal and Ethical Issues, pp. 195–205, BENTHAM SCIENCE PUBLISHERS, 2025, ISBN: 9798898813512.
@inbook{Ali_2025c,
title = {Precision Healthcare: Advancing Patient Care Through Decision Tools, Wearables, and Ethical Considerations},
author = { Shireen Adeeb Mujtaba Ali and Safia Begum and Mohammed Aleemuddin Naveed and Mohammed Naseeruddin Mujahid},
editor = {Neeraj Gupta and Abdelhameed Ibrahim and Bhavesh Vyas and Shobhna Jeet},
url = {https://www.eurekaselect.com/chapter/26828},
doi = {10.2174/9798898813512125010015},
isbn = {9798898813512},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-12-19},
urldate = {2025-12-01},
booktitle = {Precision Healthcare: Patient Care, Decision Tools, Wearables, Legal and Ethical Issues},
pages = {195–205},
publisher = {BENTHAM SCIENCE PUBLISHERS},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inbook}
}
ul Haq, Mohammed Zia; Kadloor, Parvaiz; Bangi, Sayed Mohammed Hussain
A study of clinical profile, chest X-ray, ECG changes, and 2D echocardiography in patients with chronic cor pulmonale Journal Article
In: International Journal of the Cardiovascular Academy, vol. 11, iss. 4, pp. 179-184, 2025, ISSN: 2405-819X.
@article{Haq_2025,
title = {A study of clinical profile, chest X-ray, ECG changes, and 2D echocardiography in patients with chronic cor pulmonale},
author = {Mohammed Zia ul Haq and Parvaiz Kadloor and Sayed Mohammed Hussain Bangi},
url = {https://ijcva.org/pdf/1fe4afca-adad-4137-be7c-36a5e5ab6910/articles/ijca.2025.73745/179-184.pdf},
doi = {10.4274/ijca.2025.73745},
issn = {2405-819X},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-12-12},
urldate = {2025-12-12},
journal = {International Journal of the Cardiovascular Academy},
volume = {11},
issue = {4},
pages = {179-184},
abstract = {Background and Aim: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease may result in chronic cor pulmonale, which is defined as right ventricular dilatation and/or hypertrophy resulting from pulmonary hypertension. A non-spesific clinical presentation and limited access to advanced diagnostic tools in resource-constrained settings make early diagnosis challenging. To evaluate the clinical profile and diagnostic findings from chest radiography, electrocardiography (ECG), and two-dimensional echocardiography in patients with clinically confirmed chronic cor pulmonale.
Materials and Methods: A retrospective observational study was conducted at a tertiary care center from October 2016 to September 2018. A total of 50 patients aged 30 to 80 years with clinically diagnosed chronic cor pulmonale were enrolled. Clinical symptoms, radiographic changes, ECG findings, pulmonary function tests (PFTs), and echocardiographic parameters were studied.
Results: The mean age of patients in our study was 51.7 years, with a male predominance (92%). The most common presenting features included breathlessness (100%), productive cough (100%), swelling of the feet (86%), and loss of appetite (92%). Chronic bronchitis with emphysema was the most frequent etiology, accounting for 58% of cases. Chest X-rays revealed chronic bronchitis with emphysema in 58% of patients, increased transverse cardiac diameter in 40% of patients, and a right descending pulmonary artery diameter greater than 16 mm in 62% of patients. ECG findings included right axis deviation (86%), P pulmonale (74%), low-voltage QRS complexes (52%), and arrhythmias (72%). Obstructive patterns were observed in 96% of PFTs. Echocardiography demonstrated dilation of the right ventricle and right atrium in all patients, right ventricular hypertrophy in 84% of patients, pulmonary hypertension in 90% of patients, and tricuspid regurgitation in 90% of patients. Moderate-to-severe pulmonary hypertension was observed in 74% of patients.
Conclusion: In the present study, chronic bronchitis with emphysema was the predominant cause of chronic cor pulmonale among middle-aged males. Multimodal assessment using clinical, radiographic, ECG, and echocardiographic findings enables early diagnosis. Echocardiography serves as a critical tool for evaluating right heart involvement and guiding timely intervention in chronic cor pulmonale.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Materials and Methods: A retrospective observational study was conducted at a tertiary care center from October 2016 to September 2018. A total of 50 patients aged 30 to 80 years with clinically diagnosed chronic cor pulmonale were enrolled. Clinical symptoms, radiographic changes, ECG findings, pulmonary function tests (PFTs), and echocardiographic parameters were studied.
Results: The mean age of patients in our study was 51.7 years, with a male predominance (92%). The most common presenting features included breathlessness (100%), productive cough (100%), swelling of the feet (86%), and loss of appetite (92%). Chronic bronchitis with emphysema was the most frequent etiology, accounting for 58% of cases. Chest X-rays revealed chronic bronchitis with emphysema in 58% of patients, increased transverse cardiac diameter in 40% of patients, and a right descending pulmonary artery diameter greater than 16 mm in 62% of patients. ECG findings included right axis deviation (86%), P pulmonale (74%), low-voltage QRS complexes (52%), and arrhythmias (72%). Obstructive patterns were observed in 96% of PFTs. Echocardiography demonstrated dilation of the right ventricle and right atrium in all patients, right ventricular hypertrophy in 84% of patients, pulmonary hypertension in 90% of patients, and tricuspid regurgitation in 90% of patients. Moderate-to-severe pulmonary hypertension was observed in 74% of patients.
Conclusion: In the present study, chronic bronchitis with emphysema was the predominant cause of chronic cor pulmonale among middle-aged males. Multimodal assessment using clinical, radiographic, ECG, and echocardiographic findings enables early diagnosis. Echocardiography serves as a critical tool for evaluating right heart involvement and guiding timely intervention in chronic cor pulmonale.
Fatima, Arshiya; Syed, Zaid Mazhar; Husayni, Syed Mohammed Sajjad
Evaluation of emergency laparotomy for ileocaecal emergencies a clinicopathology, prognosis, and outcome based study Journal Article
In: Journal of Contemporary Clinical Practice, vol. 11, iss. 11, pp. 1034-1039, 2025, ISSN: 2457-7200.
@article{Fatima_2025h,
title = {Evaluation of emergency laparotomy for ileocaecal emergencies a clinicopathology, prognosis, and outcome based study},
author = {Arshiya Fatima and Zaid Mazhar Syed and Syed Mohammed Sajjad Husayni},
url = {https://jccpractice.com/article/evaluation-of-emergency-laparotomy-for-ileocaecal-emergencies-a-clinicopathology-prognosis-and-outcome-based-study-1712/},
doi = {10.61336/jccp/25-11-129},
issn = {2457-7200},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-12-11},
urldate = {2025-12-11},
journal = {Journal of Contemporary Clinical Practice},
volume = {11},
issue = {11},
pages = {1034-1039},
abstract = {Background and Objectives: Ileocaecal emergencies, such as perforation, blockage, and inflammatory or viral diseases, continue to be prevalent causes of acute abdomen necessitating immediate laparotomy. These disorders are linked to considerable morbidity and mortality, particularly when diagnosis or management is postponed. The current study sought to assess the clinicopathological characteristics, surgical findings, postoperative complications, prognosis, and overall outcomes of patients receiving emergency laparotomy for ileocecal crises. Materials and Methods: Most of the 60 patients were men, and the age group with the most cases was 30 to 50 years old. 95% of the symptoms were stomach pain, followed by vomiting (72%) and stomach distension (60%). The most common causes of ileocaecal emergencies were ileal perforation (40%), typhoid perforation (25%), intestinal blockage (20%), and tuberculosis-related pathology (15%). Loop ileostomy, resection with anastomosis, and primary closure were some of the most common methods used. 35% of patients had complications after surgery, with infections at the surgery site being the most prevalent. Results: Among the 60 patients, the majority were males, with the highest incidence in the 30–50-year age group. The most common presenting symptoms were abdominal pain (95%), vomiting (72%), and abdominal distension (60%). The leading causes of ileocaecal emergencies were ileal perforation (40%), typhoid perforation (25%), intestinal obstruction (20%), and tuberculosis-related pathology (15%). Primary closure, resection with anastomosis, and loop ileostomy were the commonly performed procedures. Postoperative complications occurred in 35% of patients, with surgical site infection being the most frequent. The overall mortality rate was 10%, primarily associated with delayed presentation, septic shock, and extensive peritoneal contamination. Early surgical intervention significantly improved outcomes. Conclusion: Ileocaecal emergencies remain significant clinical issues necessitating rapid diagnosis and quick surgical intervention to mitigate morbidity and mortality. Early presentation, vigorous resuscitation, and suitable surgical interventions are crucial factors influencing positive outcomes. Improving perioperative care and making early referral systems stronger can make patients' chances of getting better even better.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Husayni, Syed Mohammed Sajjad; Fatima, Arshiya; Syed, Zaid Mazhar
Accuracy of pre-operative scoring in predicting difficulty level of laproscopic cholecystectomy Journal Article
In: Journal of Contemporary Clinical Practice, vol. 11, iss. 11, pp. 997-1008, 2025, ISSN: 2457-7200.
@article{Husayni_2025,
title = {Accuracy of pre-operative scoring in predicting difficulty level of laproscopic cholecystectomy},
author = {Syed Mohammed Sajjad Husayni and Arshiya Fatima and Zaid Mazhar Syed},
url = {https://jccpractice.com/article/accuracy-of-pre-operative-scoring-in-predicting-difficulty-level-of-laparoscopic-cholecystectomy--1706/},
doi = {10.61336/jccp/25-11-127},
issn = {2457-7200},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-12-09},
urldate = {2025-12-09},
journal = {Journal of Contemporary Clinical Practice},
volume = {11},
issue = {11},
pages = {997-1008},
abstract = {Background: Difficult laparoscopic cholecystectomy (DLC) remains a major intraoperative challenge, especially in resource-limited settings where early identification of high-risk cases is crucial for minimizing bile duct injury, operative delays, and conversion to open procedures. Although several predictive systems exist, most are derived from mixed populations or rely on subjective parameters, limiting their applicability in newly developing laparoscopic units. Objective: To validate a preoperative scoring system for predicting difficult laparoscopic cholecystectomy and to establish a modified intraoperative grading score incorporating comprehensive operative parameters. Methods: A prospective cross-sectional study was conducted on 150 patients undergoing elective laparoscopic cholecystectomy for symptomatic cholelithiasis. Preoperative variables were scored using a modified predictor scale, while intraoperative difficulty was graded using an expanded objective score incorporating adhesions, gallbladder distension, BMI, prior surgical scarring, bile/stone spillage, ductal injury, conversion, and ligature method. Diagnostic performance was assessed using sensitivity, specificity, predictive values, and ROC analysis. Multivariate logistic regression identified independent predictors of difficult LC. Results: Based on intraoperative scoring, 28.7% of patients experienced moderate–severe difficulty. The preoperative score demonstrated excellent discriminatory ability (Sensitivity 94.8%, Specificity 96.2%, AUC 0.945). The intraoperative score also performed strongly (Sensitivity 95.8%, Specificity 98.1%, AUC 0.939). Independent predictors of difficult LC included age ≥50 years, history of acute cholecystitis, BMI >30, palpable gallbladder, impacted stone, adhesions burying the gallbladder, dissection time >90 min, bile/stone spillage, and suture ligature requirement. Conclusion: Both the preoperative and modified intraoperative scoring systems demonstrated high diagnostic accuracy and reliability for predicting difficult LC. These scoring tools are simple, objective, reproducible, and particularly valuable in resource-limited settings for optimizing surgical scheduling, assigning appropriate expertise, improving patient counseling, and reducing intraoperative complications. Implementation of these scores may enhance safety and standardize difficulty assessment across surgical teams.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Hasan, Ashfaq
The Principles of Pulmonary Diagnosis: Critical Concepts and a Structured Approach Book
1, Springer Nature Singapore, 2025, ISBN: 9789819678105.
@book{Hasan_2025,
title = {The Principles of Pulmonary Diagnosis: Critical Concepts and a Structured Approach},
author = { Ashfaq Hasan},
url = {https://link.springer.com/book/10.1007/978-981-96-7810-5},
doi = {10.1007/978-981-96-7810-5},
isbn = {9789819678105},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-11-23},
urldate = {2025-11-23},
publisher = {Springer Nature Singapore},
edition = {1},
abstract = {By closely integrating pathophysiological concepts into the diagnostic process, this book adopts a strong analytical approach to the diagnosis of pulmonary diseases. A syndrome-based calibrated strategy takes into account confusing similarities and emphasizes key differences between diseases, and helps build valuable concepts that serve the clinician in unravelling diagnostic dilemmas in real-world settings.
Dedicated chapters illustrate how the incorporation of critical thinking strategies into the diagnostic reasoning process helps formulate a pragmatic differential diagnosis from a broad range of candidate conditions, with logical progression to the most likely diagnosis.
The unique format of this book provides an excellent framework for teaching, and for enhancing the diagnostic acumen of students of Pulmonary and Internal Medicine. This format also makes the book an ideal quick-reference source for pulmonologists and physicians in clinical practice.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {book}
}
Dedicated chapters illustrate how the incorporation of critical thinking strategies into the diagnostic reasoning process helps formulate a pragmatic differential diagnosis from a broad range of candidate conditions, with logical progression to the most likely diagnosis.
The unique format of this book provides an excellent framework for teaching, and for enhancing the diagnostic acumen of students of Pulmonary and Internal Medicine. This format also makes the book an ideal quick-reference source for pulmonologists and physicians in clinical practice.
Qamesa, Ubhatullah; Kishore, T. Naga Raja Ravi; Kalluri, Satya Srividya
A comparative study of conservative and surgical intervention in the management of venous leg ulcer Journal Article
In: European Journal of Cardiovascular Medicine, vol. 15, iss. 11, pp. 229-235, 2025, ISSN: 2042-4884.
@article{Qamesa_2025,
title = {A comparative study of conservative and surgical intervention in the management of venous leg ulcer},
author = {Ubhatullah Qamesa and T. Naga Raja Ravi Kishore and Satya Srividya Kalluri},
url = {https://healthcare-bulletin.co.uk/article/a-comparative-study-of-conservative-and-surgical-intervention-in-the-management-of-venous-leg-ulcer-4488/},
doi = {10.61336/ejcm/25-11-34},
issn = {2042-4884},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-11-15},
urldate = {2025-11-15},
journal = {European Journal of Cardiovascular Medicine},
volume = {15},
issue = {11},
pages = {229-235},
abstract = {Background:: Venous leg ulcers are chronic, recurring wounds of the lower limbs caused by venous hypertension and valvular incompetence. They represent a major cause of morbidity and impaired quality of life. Although conservative measures such as compression therapy and wound care promote healing, recurrence is common. Surgical correction of venous reflux may offer better long-term outcomes. This study aimed to compare conservative and surgical management in the treatment of venous leg ulcers with respect to healing rate, ulcer size reduction, and duration of recovery. Aim of the study was to evaluate and compare the efficacy of conservative and surgical management in venous ulcer healing, analyze changes in ulcer size at 1 and 2 months, and assess overall healing at 6 months. Materials and Methods: A prospective comparative study was conducted on 60 patients with venous leg ulcers, divided into two groups of 30 each. Group I (Conservative) received regular wound dressing, compression therapy, and sclerotherapy. Group II (Surgical) underwent ligation and stripping of incompetent veins or subfascial perforator ligation. Parameters such as ulcer size, duration, site, and healing status were recorded at baseline, 1 month, 2 months, and 6 months. Statistical analysis was done using unpaired t-test, Chi-square test, and ANOVA, with p < 0.05 considered significant. Results: The mean age was 58.4 ± 7.43 years in the conservative group and 56.1 ± 5.66 years in the surgical group. The medial malleolus was the most common ulcer site (82%). Mean ulcer size reduction was significantly greater in the surgical group (p < 0.0001). After two months, ulcer size decreased to 12.73 ± 2.85 mm in the surgical group and 27.73 ± 4.72 mm in the conservative group. Complete ulcer healing at six months was achieved in 90% of surgical patients and 63.3% of conservative patients (p = 0.0146). Conclusion: Surgical management provides faster and more complete healing compared to conservative methods. While conservative therapy is effective for symptom control, surgical correction of venous incompetence significantly improves healing outcomes and reduces recurrence, making it the preferred treatment modality},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Shafi, Abdul; Rahman, Shaik Faizur; Manthena, Susheel Kumar
Assessment of antibiotic usage patterns and antimicrobial resistance profiles in Emergency department infections: a cross-sectional study Journal Article
In: Journal of Chemical Health Risks, vol. 15, iss. 6, pp. 842-849, 2025, ISSN: 2251-6727.
@article{Shafi_2025,
title = {Assessment of antibiotic usage patterns and antimicrobial resistance profiles in Emergency department infections: a cross-sectional study},
author = {Abdul Shafi and Shaik Faizur Rahman and Susheel Kumar Manthena},
url = {https://www.jchr.org/index.php/JCHR/article/view/10783/5951},
issn = {2251-6727},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-11-10},
urldate = {2025-11-10},
journal = {Journal of Chemical Health Risks},
volume = {15},
issue = {6},
pages = {842-849},
abstract = {Background: Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is a critical global concern, with emergency departments (EDs) being high-risk environments for empirical antibiotic overuse. Understanding prescribing trends and their link to resistance is essential for strengthening antimicrobial stewardship practices.
Aim: To assess the antibiotic usage patterns and antimicrobial resistance profiles among patients with infections presenting to the emergency department.
Methods: A hospital-based cross-sectional study was conducted among 200 adult patients with suspected or confirmed infections presenting to the ED over one year. Data on demographics, clinical profile, antibiotic prescriptions, and microbiological findings were collected. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing was performed using standard CLSI protocols. Statistical analysis included descriptive summaries, z-tests for differences in proportions and means, and odds ratio estimation for exposure-resistance associations.
Results: Of 200 patients, 127 (63.5%) were culture-positive. Prior antibiotic exposure within 90 days was significantly associated with culture positivity (29.9% vs. 16.4%; p=0.034). Healthcare-associated isolates exhibited higher resistance rates to piperacillin-tazobactam (39.5% vs. 22.6%; p=0.045) and carbapenems (25.6% vs. 10.7%; p=0.029). Extended-spectrum β-lactamase production among Enterobacterales was significantly higher in healthcare-associated infections (67.7% vs. 45.2%; p=0.040). Guideline-concordant empirical therapy was associated with fewer multidrug-resistant isolates (OR=0.41; 95% CI 0.19-0.91; p=0.028) and lower 7-day revisit rates (8.0% vs. 21.0%; p=0.0089).
Conclusion: The study demonstrates that inappropriate or non-guideline-based antibiotic prescribing, prior exposure, and healthcare-associated settings contribute to higher resistance rates. Strengthening empirical therapy guidelines, timely de-escalation, and regular AMR surveillance in the ED can significantly improve infection outcomes and mitigate resistance trends.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Aim: To assess the antibiotic usage patterns and antimicrobial resistance profiles among patients with infections presenting to the emergency department.
Methods: A hospital-based cross-sectional study was conducted among 200 adult patients with suspected or confirmed infections presenting to the ED over one year. Data on demographics, clinical profile, antibiotic prescriptions, and microbiological findings were collected. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing was performed using standard CLSI protocols. Statistical analysis included descriptive summaries, z-tests for differences in proportions and means, and odds ratio estimation for exposure-resistance associations.
Results: Of 200 patients, 127 (63.5%) were culture-positive. Prior antibiotic exposure within 90 days was significantly associated with culture positivity (29.9% vs. 16.4%; p=0.034). Healthcare-associated isolates exhibited higher resistance rates to piperacillin-tazobactam (39.5% vs. 22.6%; p=0.045) and carbapenems (25.6% vs. 10.7%; p=0.029). Extended-spectrum β-lactamase production among Enterobacterales was significantly higher in healthcare-associated infections (67.7% vs. 45.2%; p=0.040). Guideline-concordant empirical therapy was associated with fewer multidrug-resistant isolates (OR=0.41; 95% CI 0.19-0.91; p=0.028) and lower 7-day revisit rates (8.0% vs. 21.0%; p=0.0089).
Conclusion: The study demonstrates that inappropriate or non-guideline-based antibiotic prescribing, prior exposure, and healthcare-associated settings contribute to higher resistance rates. Strengthening empirical therapy guidelines, timely de-escalation, and regular AMR surveillance in the ED can significantly improve infection outcomes and mitigate resistance trends.
Nasirabadi, Minhajzafar; Mehrukh, Arman
Kleine–Levin syndrome Journal Article
In: Telangana Journal of Psychiatry, 2025, (Published ahead-of-print).
@article{Nasirabadi_2025,
title = {Kleine–Levin syndrome},
author = {Minhajzafar Nasirabadi and Arman Mehrukh},
url = {https://journals.lww.com/tjpy/fulltext/9900/kleine_levin_syndrome.29.aspx},
doi = {10.4103/tjp.tjp_26_25},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-11-07},
urldate = {2025-11-07},
journal = {Telangana Journal of Psychiatry},
abstract = {Kleine–Levin syndrome (KLS) is a rare sleep disorder marked by recurrent hypersomnolent episodes and behavioral changes with unclear etiology. We report a 45-year-old male with severe, early-onset KLS – episodes lasting 20 days and recurring monthly since age 10. Symptoms included hypersomnolence, derealization, hypersexuality, aggression on forced arousal, and interepisode depression. His history includes childhood Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) and early traumatic brain injury (TBI). Despite trials of various psychotropic medications, symptoms persisted. This case suggests a possible link among ADHD, TBI, and KLS. While ADHD and narcolepsy share neurobiological features – and narcolepsy overlaps with KLS – the role of genetic or neurodevelopmental factors in KLS remains uncertain. The patient’s trajectory raises the hypothesis of an interaction between ADHD, narcolepsy, and KLS, though this may be coincidental. This report contributes to the limited literature on severe, early-onset KLS and underscores the need for further research into potential neurodevelopmental and traumatic risk factors.},
note = {Published ahead-of-print},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Hadi, Mohammad Abdul; Arifuddin, Mehnaaz Sameera; Hazari, Mohammed Abdul Hannan
Evaluation of body weight/body mass index as a predictor of dengue severity in children Journal Article
In: Annals of Medical Physiology, vol. 8, iss. 1, pp. 7-13, 2025, ISSN: 2456-8422.
@article{Hadi_2025,
title = {Evaluation of body weight/body mass index as a predictor of dengue severity in children},
author = {Mohammad Abdul Hadi and Mehnaaz Sameera Arifuddin and Mohammed Abdul Hannan Hazari},
url = {https://amphysiol.com/index.php/amp/article/view/v8i1.00076/2025_7_13.pdf},
doi = {10.23921/amp.2025v8i1.00076},
issn = {2456-8422},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-10-31},
urldate = {2025-10-31},
journal = {Annals of Medical Physiology},
volume = {8},
issue = {1},
pages = {7-13},
abstract = {Higher body mass index (BMI) is a risk factor for many non-communicable diseases and certain infectious diseases. Very less evidence is available that links body mass with dengue severity especially in children. The aim of this study was to evaluate any association between body weight/body mass index of children with severity of dengue illness. A retrospective, medical-records based observational study was conducted on 100 dengue-infected children in the age group of 2-15 years between August and October 2023. Dengue serology, complete blood picture, liver enzymes and coagulation profile were noted along with recording of anthropometric parameters like height and weight at the time of admission. Based on clinical presentation, patients were classified as severe and non-severe dengue. Most of the admitted dengue infected children belonged to underweight (67%) and normal weight (27%) category. The patients were divided into 2 groups: Group 1 included patients in the age group of 2-5 years where the independent variable considered was z-score for weight-for-age and Group 2 included patients between >5-15 years where z-score for BMI-for-age was taken as independent variable. Binomial logistic regression analysis was done to correctly classify the cases as non-severe and severe based on z-scores of weight-for-age / BMI-for-age (independent variable) of the effected children which was statistically significant in group 2 (p=0.000). The model correctly classified 61.8% of cases in group 1 and 86.4% of cases in group 2. Though the majority of cases were in underweight or normal weight category, the results indicate that those with higher weight and BMI for their age and gender are more likely to develop severe dengue infection.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Begum, Syeda Tasneem; Basith, Mohammed Abdul; Durdana, Asfa; Hasan, Ashfaq; Naveed, Mohammed Aleemuddin; Briek, Fahad Abdullah Bin; Ahmed, Syed Mahmood; Ali, Shireen Adeeb Mujtaba
Spontaneous pneumomediastinum in acute severe asthma: A case report Journal Article
In: Journal of Dr. NTR University of Health Sciences, vol. 14, iss. 4, pp. 434–437, 2025, ISSN: 2277-8632.
@article{Begum_2025b,
title = {Spontaneous pneumomediastinum in acute severe asthma: A case report},
author = { Syeda Tasneem Begum and Mohammed Abdul Basith and Asfa Durdana and Ashfaq Hasan and Mohammed Aleemuddin Naveed and Fahad Abdullah Bin Briek and Syed Mahmood Ahmed and Shireen Adeeb Mujtaba Ali},
url = {https://journals.lww.com/jdrntruhs/fulltext/2025/10000/spontaneous_pneumomediastinum_in_acute_severe.13.aspx},
doi = {10.4103/jdrntruhs.jdrntruhs_37_24},
issn = {2277-8632},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-10-31},
urldate = {2025-10-01},
journal = {Journal of Dr. NTR University of Health Sciences},
volume = {14},
issue = {4},
pages = {434–437},
publisher = {Wolters Kluwer Health},
abstract = {Spontaneous pneumomediastinum (SPM), also known as mediastinal emphysema, develops as a consequence of acute severe asthma and is an uncommon entity. It is essential to recognize this complication since it must be distinguished from other potentially fatal illnesses. The purpose of presenting this case report is to highlight its importance, consider it in the differential diagnosis (d/d) of various problems resulting from acute severe asthma, and provide a detailed explanation of its management strategy.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Kishore, T. Naga Raja Ravi; Anjum, Ishrath; Syed, Zaid Mazhar; Kalluri, Satya Srividya; Harooni, Syed Asif Shah
Revalidating preoperative prediction score and to develop a more accurate prediction score-to predict difficult cholecystectomy Journal Article
In: Journal of Contemporary Clinical Practice, vol. 11, iss. 10, pp. 648-657, 2025, ISSN: 2457-7200.
@article{Kishore_2025,
title = {Revalidating preoperative prediction score and to develop a more accurate prediction score-to predict difficult cholecystectomy},
author = {T. Naga Raja Ravi Kishore and Ishrath Anjum and Zaid Mazhar Syed and Satya Srividya Kalluri and Syed Asif Shah Harooni},
url = {https://jccpractice.com/article/revalidating-preoperative-prediction-score-and-to-develop-a-more-accurate-prediction-score-to-predict-difficult-cholecystectomy-1502/},
doi = {10.61336/jccp/25-10-89},
issn = {2457-7200},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-10-24},
urldate = {2025-10-24},
journal = {Journal of Contemporary Clinical Practice},
volume = {11},
issue = {10},
pages = {648-657},
abstract = {Background: Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is the gold standard for symptomatic gallstone disease due to its minimally invasive nature and faster recovery. However, intraoperative challenges can increase the risk of conversion and complications. Predicting surgical difficulty preoperatively enables better planning and patient safety. This study aimed to design and validate a scoring system to predict laparoscopic cholecystectomy difficulty using clinical and imaging parameters. Materials and Methods: A prospective study was conducted on 50 patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy at Princess Esra Hospital and Owaisi Hospital & Research Centre, Hyderabad, after obtaining ethical clearance. Clinical, biochemical, and imaging findings were analyzed, and scoring parameters were formulated to predict surgical difficulty. Results and Observations: Most patients were young adults (19–30 years) and female (76%), presenting predominantly with right hypochondrial pain and dyspeptic symptoms. Imaging revealed gallbladder wall thickening, CBD stones, and inflammatory changes in select cases. A scoring system comprising 21 preoperative and 13 intraoperative parameters was developed, stratifying patients into three risk categories: Very Low (0–6), Low to Moderate (7–14), and Moderate to High (15–30). Higher scores correlated with increased surgical difficulty and conversion rates. Conclusion: Laparoscopic cholecystectomy remains the safest and most effective treatment for gallbladder disease. The proposed scoring system provides a simple and reliable tool to predict operative difficulty, allowing for better surgical planning, appropriate allocation of resources, and improved patient outcomes},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Kishore, T. Naga Raja Ravi; Kalluri, Satya Srividya; Sarveswaran, Venugopal
A prospective study on independent risk factors for lower limb amputation in diabetic foot patients Journal Article
In: European Journal of Cardiovascular Medicine, vol. 15, iss. 10, pp. 405-411, 2025, ISSN: 2042-4884.
@article{Kishore_2025b,
title = {A prospective study on independent risk factors for lower limb amputation in diabetic foot patients},
author = {T. Naga Raja Ravi Kishore and Satya Srividya Kalluri and Venugopal Sarveswaran},
url = {https://healthcare-bulletin.co.uk/article/a-prospective-study-on-independent-risk-factors-for-lower-limb-amputation-in-diabetic-foot-patients-4388/},
doi = {10.61336/ejcm/25-10-71},
issn = {2042-4884},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-10-22},
urldate = {2025-10-22},
journal = {European Journal of Cardiovascular Medicine},
volume = {15},
issue = {10},
pages = {405-411},
abstract = {Background: Diabetic foot remains one of the most serious complications of diabetes mellitus, often leading to infection, ulceration, gangrene, and limb amputation. It reflects a complex interaction between neuropathy, ischemia, and infection. Early identification of risk factors is essential for prevention and limb preservation. Aim of the study was to identify and quantify the independent risk factors associated with lower limb amputation among patients with diabetic foot disease. Materials and Methods: This prospective descriptive analytic study was conducted at the Department of General Surgery, Sri Ramakrishna Hospital, Coimbatore, from November 2014 to November 2016. A total of 150 diabetic foot patients aged 18–80 years were included. Clinical evaluation, laboratory investigations, Doppler ultrasonography, and culture studies were performed. Variables such as age, sex, duration of diabetes, HbA1C level, peripheral vascular disease (PVD), neuropathy, smoking, foot deformities, and comorbid illnesses were analyzed. Statistical analysis was done using SPSS version 17.0, with p < 0.05 considered significant. Results: Among the 150 patients, 98 (65.3%) were males and 52 (34.7%) females, with the majority in the 51–60-year age group. Neuropathy was observed in 40%, and ischemia in 35.3% of patients. Overall, 74 patients (49.3%) required amputation—24 (16%) major and 50 (33.3%) minor—while 76 (50.7%) were managed conservatively. Foot infections were present in 68.6%, with Pseudomonas (15.3%) and Staphylococcus aureus (12.7%) being the most common pathogens. Univariate analysis revealed smoking, PVD, neuropathy, higher PEDIS grade (>3), and associated comorbidities as significant predictors of amputation (p < 0.05), whereas duration of diabetes, HbA1C level, previous amputation, and foot deformities were not statistically significant. Conclusion: Neuropathy, ischemia, and infection remain the principal determinants of amputation in diabetic foot disease. Smoking and systemic comorbidities further increase the risk. Early detection, strict glycemic control, proper foot care, and a multidisciplinary approach are essential to prevent limb loss and improve outcomes in diabetic patients.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Ali, Syed Mubid; Masood, Mohammed Abdullah; Tazeen, Naushaba; Tabassum, Asiya; Afroze, Idrees Akhtar; Begum, Atiya; Ali, Shireen Adeeb Mujtaba
Rare meets routine: a case of sessile serrated lesion presenting as acute appendicitis Journal Article
In: Indian Journal of Pathology and Oncology, vol. 12, iss. 3, pp. 279-282, 2025, ISSN: 2394-6784.
@article{Ali_2025b,
title = {Rare meets routine: a case of sessile serrated lesion presenting as acute appendicitis},
author = {Syed Mubid Ali and Mohammed Abdullah Masood and Naushaba Tazeen and Asiya Tabassum and Idrees Akhtar Afroze and Atiya Begum and Shireen Adeeb Mujtaba Ali},
url = {https://ijpo.co.in/archive/volume/12/issue/3/article/24927/pdf},
doi = {10.18231/j.ijpo.11098.1680662831},
issn = {2394-6784},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-10-17},
urldate = {2025-10-17},
journal = {Indian Journal of Pathology and Oncology},
volume = {12},
issue = {3},
pages = {279-282},
abstract = {Sessile serrated lesions (SSLs) are rare premalignant neoplasms usually arising in the colon but can also occur in the appendix, where their presentation often mimics acute appendicitis. We report the case of a 68‑year‑old male who presented with right lower abdominal pain and imaging findings suggestive of acute appendicitis with appendicular mucocele. The patient underwent appendectomy, and histopathological examination of the resected specimen revealed a sessile serrated lesion with marked dysplasia, without evidence of adenocarcinoma. Appendiceal SSLs are seldom reported in literature and may be overlooked due to their nonspecific clinical and radiological features. As SSLs are important precursors of colorectal carcinoma via the serrated neoplasia pathway, meticulous histopathological evaluation is crucial for accurate diagnosis. Early recognition, surgical excision, and colonoscopic follow‑up can help prevent malignant transformation. This case adds to the limited literature on appendiceal SSLs and emphasizes the need for increased awareness and documentation.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Atharuddin, Athar Mohammed; Faraz, Neda; Fatima, Arshiya
A comparative study of wound healing and complications with the use of 1-0 vicryl vs 1-0 prolene for rectus closure Journal Article
In: Journal of Contemporary Clinical Practice, vol. 11, iss. 10, pp. 372-380, 2025, ISSN: 2457-7200.
@article{Atharuddin_2025,
title = {A comparative study of wound healing and complications with the use of 1-0 vicryl vs 1-0 prolene for rectus closure},
author = {Athar Mohammed Atharuddin and Neda Faraz and Arshiya Fatima},
url = {https://jccpractice.com/article/a-comparative-study-of-wound-healing-and-complications-with-the-use-of-1-0-vicryl-vs-1-0-prolene-for-rectus-closure-1458/},
doi = {10.61336/jccp/25-10-55},
issn = {2457-7200},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-10-15},
urldate = {2025-10-15},
journal = {Journal of Contemporary Clinical Practice},
volume = {11},
issue = {10},
pages = {372-380},
abstract = {Background: Surgery and sutures are inseparable. Down the ages, newer and more efficacious suture materials and techniques have been introduced. Among all wound closures, abdominal wound closure is the most challenging task for a surgeon. There are different techniques according to suture material, suturing technique and length of suture material that have been suggested optimal for rectus closure. These prospects are still under study and are controversial. This study was to compare the efficacy of vicryl and prolene for rectus closure by studying the wound healing and complication rates (wound infection, wound dehiscence, burst abdomen etc). Materials and Methods: The present prospective comparative study was conducted on patients admitted for surgeries in the Department of General surgery, Deccan College Of Medical Sciences, Hyderabad. for a period of 18 months. Prior to the initiation of the study, Ethical and Research Committee clearance was obtained from Institutional Ethical Committee. During present study total 50 patients meeting inclusion criteria were enrolled into the study. Results and observations: There was no statistical difference between the groups in terms of age (p: 0.1358); gender (p: 1.131); diabetic status (p: 1.1532); BMI (p: 1.1611); type of surgery (p: 0.8321); duration of surgery (p: 0.8321); intra operative hypotension prevalence (p: 0.1352); type of incisions (p: 1.3521); type of surgical site infections (p: 0.06). The incidence of burst abdomen (p: 0.01) was high in group B, day of burst abdomen incidence (p: 0.02), incidence of surgical site infections high in group B (p: 0.01); rate of wound healing was slow in group B (p: 0.001) Conclusion: From the present study we conclude that non-absorbable suture (prolene) was better in terms of wound healing and cosmesis as compared to absorbable suture used (vicryl) taking into consideration the points: wound dehiscence, burst abdomen incidence, surgical site infections incidence was higher in group B comparatively. Group B subjects had a slower rate of wound healing comparatively.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Siddiqui, Shadma; Khan, Mohammed Zeeshan Ali; Nasirabadi, Minhajzafar; Uddin, Ahmed Mubariz
Mental health behind bars: psychiatric morbidity among female prisoners in Southern India Journal Article
In: Telangana Journal of Psychiatry, 2025, ISSN: 2455-8559, (Published ahead-of-print).
@article{Siddiqui_2025,
title = {Mental health behind bars: psychiatric morbidity among female prisoners in Southern India},
author = {Shadma Siddiqui and Mohammed Zeeshan Ali Khan and Minhajzafar Nasirabadi and Ahmed Mubariz Uddin},
url = {https://journals.lww.com/tjpy/fulltext/9900/mental_health_behind_bars__psychiatric_morbidity.21.aspx},
doi = {10.4103/tjp.tjp_3_25},
issn = {2455-8559},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-10-14},
urldate = {2025-10-14},
journal = {Telangana Journal of Psychiatry},
abstract = {Background: Prisoners endure life in confinement, separated from society. The harsh living conditions and stressful environment in prisons, among various other factors, increase the likelihood of inmates developing mental disorders. Female prisoners frequently encounter heightened psychosocial challenges due to a combination of factors, including the demanding prison environment and insufficient familial support. Hence, the present study was conducted to identify the prevalence of psychiatric morbidity in female prisoners.
Subjects and Methods: A cross-sectional study was done among convicted female inmates of the Central Prison of Telangana after taking consent and required permissions from authority. The Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale (BPRS) was used to assess psychiatric morbidity among 82 female prisoners.
Results: The mean age (± standard deviation) of the study population was 44.42 (±14.12) years. The prevalence of psychiatric morbidity according to BPRS scoring was 76.83%. 54.87% showed somatic concerns, 43.90% depressive symptoms, 30.48% anxiety symptoms, and feelings of guilt present in 21.95%. Psychotic symptoms such as suspiciousness present in 6.09%, hallucinatory behavior in 2.43%, unusual thought content in 5%, blunted affect in 2.43%, and conceptual disorganization in 6.09%. Grandiosity present in one candidate and multiple psychiatric symptoms were observed in many candidates.
Conclusion: Within most societies, people with mental disorders face stigma and discrimination. This stigma usually persists in prison, with the person facing isolation due to imprisonment, further affecting their mental health. Data from the study suggest a high prevalence of psychiatric morbidity among female prisoners. Data from the study suggests a high prevalence of psychiatric morbidity among female prisoners, with somatic symptoms being the most common, followed by depressive symptoms. Many candidates had multiple psychiatric symptoms present simultaneously. There is a need for proper identification and treatment of mental illness among this underprivileged group.},
note = {Published ahead-of-print},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Subjects and Methods: A cross-sectional study was done among convicted female inmates of the Central Prison of Telangana after taking consent and required permissions from authority. The Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale (BPRS) was used to assess psychiatric morbidity among 82 female prisoners.
Results: The mean age (± standard deviation) of the study population was 44.42 (±14.12) years. The prevalence of psychiatric morbidity according to BPRS scoring was 76.83%. 54.87% showed somatic concerns, 43.90% depressive symptoms, 30.48% anxiety symptoms, and feelings of guilt present in 21.95%. Psychotic symptoms such as suspiciousness present in 6.09%, hallucinatory behavior in 2.43%, unusual thought content in 5%, blunted affect in 2.43%, and conceptual disorganization in 6.09%. Grandiosity present in one candidate and multiple psychiatric symptoms were observed in many candidates.
Conclusion: Within most societies, people with mental disorders face stigma and discrimination. This stigma usually persists in prison, with the person facing isolation due to imprisonment, further affecting their mental health. Data from the study suggest a high prevalence of psychiatric morbidity among female prisoners. Data from the study suggests a high prevalence of psychiatric morbidity among female prisoners, with somatic symptoms being the most common, followed by depressive symptoms. Many candidates had multiple psychiatric symptoms present simultaneously. There is a need for proper identification and treatment of mental illness among this underprivileged group.
Ayesha, Syeda; Ahmed, Waseem; Hashmi, Khurram Adil
Assessment of hearing impairment in patients with allergic rhinitis through audiological profile Journal Article
In: International Journal of Medicine and Public Health, vol. 15, iss. 3, pp. 2118-2121, 2025, ISSN: 2230-8598.
@article{Ayesha_2025c,
title = {Assessment of hearing impairment in patients with allergic rhinitis through audiological profile},
author = {Syeda Ayesha and Waseem Ahmed and Khurram Adil Hashmi},
url = {https://www.ijmedph.org/Uploads/Volume15Issue3/391.%203001.%20IJMEDPH_Shubham%20Jaju_2118-2121.pdf},
doi = {10.70034/ijmedph.2025.3.391 },
issn = {2230-8598},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-09-30},
urldate = {2025-09-30},
journal = {International Journal of Medicine and Public Health},
volume = {15},
issue = {3},
pages = {2118-2121},
abstract = {Background: Allergic rhinitis (AR) is a common chronic inflammatory disorder affecting the upper respiratory tract, which may also impair auditory function through Eustachian tube dysfunction and middle ear involvement. Despite increasing awareness, its impact on hearing remains under-recognized. To assess the audiological profile of patients with allergic rhinitis using tympanometry and pure tone audiometry, and to explore the correlation between hearing thresholds and duration of AR symptoms.
Materials and Methods: This cross-sectional, hospital-based study included 150 patients with clinically diagnosed allergic rhinitis and 150 age-matched controls. Audiological evaluation was conducted using the Titan Interacoustic Tympanometer and standard pure tone audiometry. Tympanogram types, air conduction thresholds, and degrees of hearing loss were compared. Pearson correlation was used to analyze the relationship between symptom duration and hearing thresholds.
Results: AR patients had significantly more abnormal tympanograms (Type B: 20.7%, Type C: 10%) compared to controls (Type B: 3.3%, Type C: 4.7%) (p < 0.001). Air conduction thresholds were elevated across all frequencies in the AR group (p < 0.001), with a mean threshold of 30.5 ± 8.2 dB at 8000 Hz. Hearing loss was detected in 32% of AR patients—predominantly mild (22.7%) and moderate (6.7%). A moderate positive correlation (r = 0.41, p < 0.001) was found between duration of AR and hearing loss severity.
Conclusion: Allergic rhinitis is significantly associated with subclinical conductive hearing loss and abnormal middle ear function, which worsen with prolonged symptom duration. Early audiological screening in AR patients is essential to prevent long-term auditory complications.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Materials and Methods: This cross-sectional, hospital-based study included 150 patients with clinically diagnosed allergic rhinitis and 150 age-matched controls. Audiological evaluation was conducted using the Titan Interacoustic Tympanometer and standard pure tone audiometry. Tympanogram types, air conduction thresholds, and degrees of hearing loss were compared. Pearson correlation was used to analyze the relationship between symptom duration and hearing thresholds.
Results: AR patients had significantly more abnormal tympanograms (Type B: 20.7%, Type C: 10%) compared to controls (Type B: 3.3%, Type C: 4.7%) (p < 0.001). Air conduction thresholds were elevated across all frequencies in the AR group (p < 0.001), with a mean threshold of 30.5 ± 8.2 dB at 8000 Hz. Hearing loss was detected in 32% of AR patients—predominantly mild (22.7%) and moderate (6.7%). A moderate positive correlation (r = 0.41, p < 0.001) was found between duration of AR and hearing loss severity.
Conclusion: Allergic rhinitis is significantly associated with subclinical conductive hearing loss and abnormal middle ear function, which worsen with prolonged symptom duration. Early audiological screening in AR patients is essential to prevent long-term auditory complications.
Idris, Ahmed Sifeeldein Ahmed; Nashrah, Umme; Amara, Umme; Shaikh, Nissar
Eustachian valve endocarditis in patients with fournier’s gangrene and septic shock: a rare case and a literature review Journal Article
In: Qatar Medical Journal, vol. 2025, iss. 3, pp. 93, 2025, ISSN: 0253-8253.
@article{Idris_2025,
title = {Eustachian valve endocarditis in patients with fournier’s gangrene and septic shock: a rare case and a literature review },
author = {Ahmed Sifeeldein Ahmed Idris and Umme Nashrah and Umme Amara and Nissar Shaikh},
url = {https://www.qscience.com/docserver/fulltext/qmj/2025/3/qmj.2025.93.pdf?expires=1759819401&id=id&accname=guest&checksum=1C92FB251CA567B82A4BCC00C75DACF1},
doi = {10.5339/qmj.2025.93},
issn = {0253-8253},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-09-15},
urldate = {2025-09-15},
journal = {Qatar Medical Journal},
volume = {2025},
issue = {3},
pages = {93},
abstract = {Introduction: The eustachian valve (EV) is a remnant of the right sinus venosus valve. It remains different in size and shape without much impact on adult life. In 5% to 10% of all endocarditis, are seen in the right side of the heart is involved, which is rare compared to the left side of the heart. Bacteremia, central venous catheter, heart implants, and drug abuse increase the risk of EV vegetation and right heart endocarditis. We are reporting a case of EV endocarditis in patients with Fournier’s gangrene and septic shock. Case Presentation: A 45-year-old male patient was admitted into the surgical intensive care unit with Fournier’s gangrene, septic shock, and acute kidney injury (AKI). The patient was managed by invasive ventilation, noradrenaline, vasopressin, and renal replacement therapy. He developed Escherichia coli bacteremia and candidemia. We added meropenem and antifungal to the therapy. The transthoracic echocardiography showed EV vegetation and thread-like vegetation in the right coronary sinus, which was confirmed with transesophageal echocardiography. With aggressive therapies, the patient recovered from septic shock, organ dysfunction and was successfully liberated from invasive ventilation. The patient was discharged home on day 27. The antibiotics and antifungal were continued for 6 weeks. Two weeks after discharge, the follow-up echocardiogram was normal, and he was doing well. Discussion: Eustachian valve endocarditis is rare, and should be treated with appropriate, culture- and sensitivity-guided antibiotics and or antifungal therapy for 6 weeks. The outcome of EV vegetations of endocarditis is good. The reported mortality is up to 17%. The independent risk factors associated with mortality are AKI, the Charlson comorbidity index, congestive heart failure, larger vegetation, and central nervous system involvement. Conclusion: The presence of larger EV, along with E. coli (ESBL) bacteremia and fungemia, increases the risk of right-sided endocarditis, which is rarely reported. Our patient was diagnosed early, received appropriate antimicrobial treatment for a sufficient duration, resulting in a better outcome. A high index of suspicion, along with early diagnosis and culture-guided 6-week antimicrobial therapy, will improve the patient’s outcomes.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Fatima, Sarwat; Handa, Deepika
Humoral immune response to COVID-19 vaccine in health care workers and the factors influencing it during vaccine drive - a cross-sectional study Journal Article
In: IP International Journal of Medical Microbiology and Tropical Diseases, vol. 11, iss. 3, pp. 323-329, 2025, ISSN: 2581-4753.
@article{Fatima_2025e,
title = {Humoral immune response to COVID-19 vaccine in health care workers and the factors influencing it during vaccine drive - a cross-sectional study},
author = {Sarwat Fatima and Deepika Handa},
url = {https://ijmmtd.org/archive/volume/11/issue/3/article/24512/pdf},
doi = {10.18231/j.ijmmtd.v.11.i.3.15 },
issn = {2581-4753},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-09-04},
urldate = {2025-09-04},
journal = {IP International Journal of Medical Microbiology and Tropical Diseases},
volume = {11},
issue = {3},
pages = {323-329},
abstract = {Background: The COVID-19 vaccine drive by the public healthcare system had several safety and efficacy concerns in the minds of health care workers and common man for several vague reasons.
Objective: In this context; the study was planned to determine the humoral immune response in the vaccine recipients of the first indigenously prepared vaccines in India [Covaxin & Covishield]. And, to know the influence of various factors on it. Lastly, to note the adverse events reported by the recipients if any.
Materials and Methods: A cross-sectional point prevalence study with simple convenient sampling method was designed. Baseline data on demographics, presence of comorbid conditions, vaccination details, adverse events to vaccine and information on presence of COVID-19 disease in the past 3-6 months was obtained from participants using a validated questionnaire. Institutional ethical clearance was obtained. The participants’ inclusion and exclusion criteria were established. SARS-CoV-2 IgG antibody was determined using ELFA method. Antibody index was estimated and used for interpretation of the test results. Statistical R software was used for data analysis.
Results: of the 86 participants, 84 were found eligible for enrollment. Male to female ratio was 0.9:1. The study participants were in the age group from 20-80 years. Around 29/84[34.52%] had comorbid conditions and the commonest comorbid conditions was hypertension. Overall, 72/84 [86%] of the HCWs were seropositive following vaccination. Greater number of fully vaccinated HCWs 60/62 [97%] were seropositive than partially vaccinated 12/22 [54%] with a p value of 0.001 and their corresponding antibody index was also higher. Among the various variables studied age, gender and presence of comorbid conditions the last one had a positive impact on seropositivity and antibody index values. Mild adverse events following vaccination were noted in majority. However, the antibody index was higher for them than in participants with no adverse events.
Conclusion: Our study highlights the efficacy and safety of vaccine by demonstrating seroconversion in 86% of the recipients and clears the vaccine hesitancy from the minds of HCWs and common man as well.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Objective: In this context; the study was planned to determine the humoral immune response in the vaccine recipients of the first indigenously prepared vaccines in India [Covaxin & Covishield]. And, to know the influence of various factors on it. Lastly, to note the adverse events reported by the recipients if any.
Materials and Methods: A cross-sectional point prevalence study with simple convenient sampling method was designed. Baseline data on demographics, presence of comorbid conditions, vaccination details, adverse events to vaccine and information on presence of COVID-19 disease in the past 3-6 months was obtained from participants using a validated questionnaire. Institutional ethical clearance was obtained. The participants’ inclusion and exclusion criteria were established. SARS-CoV-2 IgG antibody was determined using ELFA method. Antibody index was estimated and used for interpretation of the test results. Statistical R software was used for data analysis.
Results: of the 86 participants, 84 were found eligible for enrollment. Male to female ratio was 0.9:1. The study participants were in the age group from 20-80 years. Around 29/84[34.52%] had comorbid conditions and the commonest comorbid conditions was hypertension. Overall, 72/84 [86%] of the HCWs were seropositive following vaccination. Greater number of fully vaccinated HCWs 60/62 [97%] were seropositive than partially vaccinated 12/22 [54%] with a p value of 0.001 and their corresponding antibody index was also higher. Among the various variables studied age, gender and presence of comorbid conditions the last one had a positive impact on seropositivity and antibody index values. Mild adverse events following vaccination were noted in majority. However, the antibody index was higher for them than in participants with no adverse events.
Conclusion: Our study highlights the efficacy and safety of vaccine by demonstrating seroconversion in 86% of the recipients and clears the vaccine hesitancy from the minds of HCWs and common man as well.
Singhal, Rohan; Ghadvaje, Gayatri; Karra, Nanditha; Gadde, Sai Teja; Chandra, Prerna; Voruganti, Bharat Krishna Teja; Doddareddy, Navya Pillikunte; Iftikhar, Sadaf; Patel, Tirath
A narrative review on fecal microbiota transplantation routes in ulcerative colitis: identifying the optimal approach across key parameters Journal Article
In: Annals of Medicine & Surgery, vol. 87, iss. 10, pp. 6599-6611, 2025, ISSN: 2049-0801.
@article{Singhal_2025,
title = {A narrative review on fecal microbiota transplantation routes in ulcerative colitis: identifying the optimal approach across key parameters},
author = {Rohan Singhal and Gayatri Ghadvaje and Nanditha Karra and Sai Teja Gadde and Prerna Chandra and Bharat Krishna Teja Voruganti and Navya Pillikunte Doddareddy and Sadaf Iftikhar and Tirath Patel},
url = {https://journals.lww.com/annals-of-medicine-and-surgery/abstract/9900/a_narrative_review_on_fecal_microbiota.3380.aspx},
doi = {10.1097/ms9.0000000000003841},
issn = {2049-0801},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-09-02},
urldate = {2025-09-02},
journal = {Annals of Medicine & Surgery},
volume = {87},
issue = {10},
pages = {6599-6611},
abstract = {Fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) has gained increasing attention as a novel therapeutic approach for treating ulcerative colitis (UC), a chronic inflammatory bowel disease that causes an imbalance in the gut microbiota. Although FMT has demonstrated the potential to induce remission in UC patients, the most effective route of administration remains an area of active investigation. This narrative review provides a comprehensive comparison of different FMT delivery methods, such as oral capsules, enemas, colonoscopy, and nasogastric or nasoenteric tubes, across a range of clinically relevant parameters, including efficacy, safety, patient satisfaction, microbiota changes, pretreatment protocols, and cost-effectiveness. Furthermore, we examined how post-FMT dietary interventions may influence microbial engraftment and improve the long-term outcomes in patients with UC. In addition to assessing these practical and clinical factors, this review highlights the importance of patient-centered considerations, such as the tolerability and convenience of each administration route. The integration of these findings can provide valuable insights into how different FMT routes affect disease outcomes and guide clinicians in optimizing the treatment for individual patients. By synthesizing current evidence on these key variables, we aimed to identify the most effective and feasible FMT approach for UC. Establishing standardized protocols for FMT administration, informed by this analysis, will be crucial for ensuring consistency in clinical practice, improving patient outcomes, and minimizing adverse events. The insights from this review will help pave the way for more targeted and individualized FMT strategies, ultimately enhancing the therapeutic landscape of UC management.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Chaudhry, Waleed Razzaq; Altaf, Sana; Mohammed, Cara; Fuerte, Sofia
Fetal-maternal complications due to pregnancy-acquired tuberculosis: a narrative review of the literature Journal Article
In: Monaldi Archives for Chest Disease, 2025, ISSN: 1122-0643, (Online ahead of print).
@article{Chaudhry_2025,
title = {Fetal-maternal complications due to pregnancy-acquired tuberculosis: a narrative review of the literature},
author = {Waleed Razzaq Chaudhry and Sana Altaf and Cara Mohammed and Sofia Fuerte},
url = {https://www.monaldi-archives.org/macd/article/view/3126/2125},
doi = {10.4081/monaldi.2025.3126},
issn = {1122-0643},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-09-01},
urldate = {2025-09-01},
journal = {Monaldi Archives for Chest Disease},
abstract = {Tuberculosis (TB) during pregnancy can cause certain deleterious effects to both the mother and the fetus, leading to significant morbidity and mortality. The risk of TB rises significantly during pregnancy due to dampening of the immune response in females and certain factors yet to be studied. Since pregnant females are ruled out of clinical trials due to their pregnancy status, not much clinical data is available on how to combat TB in them or about the clinical safety and efficacy of certain drugs. Hence, not only is it important to make pregnant females vital study participants of clinical trials, but also to enhance their knowledge regarding the disease so that they may timely access quality care. It is also important to facilitate these TB-positive pregnant females through the introduction of gender-sensitive policies that are more exclusive and allow access to quality TB control programs that provide timely care, nutritional support, and quality and supportive management.},
note = {Online ahead of print},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Hazari, Mohammed Abdul Hannan; Rao, Kailas Laxman; Tazneem, Bachi; Rafeeq, Sana; Fatima, Syeda Rahmath; Jabeen, Summaya; Kavya, Kankan
Correlation of comorbidities and outcome in CAD patients: a novel TANGENTS score study Journal Article
In: Military Medical Science Letters, vol. 94, iss. 3, pp. 107-114, 2025, ISSN: 0372-7025.
@article{Hazari_2025,
title = {Correlation of comorbidities and outcome in CAD patients: a novel TANGENTS score study},
author = {Mohammed Abdul Hannan Hazari and Kailas Laxman Rao and Bachi Tazneem and Sana Rafeeq and Syeda Rahmath Fatima and Summaya Jabeen and Kankan Kavya},
url = {https://mmsl.cz/artkey/mms-202503-0002_correlation-of-comorbidities-and-outcome-in-cad-patients-a-novel-tangents-score-study.php},
doi = {10.31482/mmsl.2024.009},
issn = {0372-7025},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-09-01},
urldate = {2024-06-18},
journal = {Military Medical Science Letters},
volume = {94},
issue = {3},
pages = {107-114},
publisher = {Faculty of Military Health Sciences, University of Defence, Czech Republic},
abstract = {Background: Cardiovascular diseases (CVD) are influenced by various established risk factors, including the ratio of neutrophils to lymphocytes and platelets, which has been shown to be an independent risk factor for acute coronary syndrome (ACS). This study aims to create a new scoring system called TANGENTS that utilizes discrete parameters of risk factors and diagnostic parameters to analyze the outcome of coronary artery disease (CAD) patients with comorbidities, particularly Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods: We included 151 subjects (mean age 57.92 ± 23.86) who presented with ST-elevation and ST-depression on admission and were treated with heparin, clopidogrel, aspirin, and atorvastatin while undergoing all the necessary diagnostic tests. We obtained ECG and complete blood picture (CBP) results on admission, day 3, and day of discharge.
Results: ST-depression on ECG on day-1 was 0.35 and decreased to 0.30 on the day of discharge. ST-elevation on ECG on day-1 was -0.89 and decreased to -0.16 on the day of discharge. The average neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NPR) was 0.49, which was high in 144 patients. The mean NLR value was 5.52, indicating a correlation between high NLR values and the magnitude of current injury on admission.
Conclusion: The TANGENTS scoring system can be used as an early evaluation tool for CAD patients with comorbidities to manage and prevent further complications. It allows for progressive differentiation in the severity of clinical outcomes using all the parameters of the score, and the parameters creating the TANGENTS score scale were found to be reliable.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Methods: We included 151 subjects (mean age 57.92 ± 23.86) who presented with ST-elevation and ST-depression on admission and were treated with heparin, clopidogrel, aspirin, and atorvastatin while undergoing all the necessary diagnostic tests. We obtained ECG and complete blood picture (CBP) results on admission, day 3, and day of discharge.
Results: ST-depression on ECG on day-1 was 0.35 and decreased to 0.30 on the day of discharge. ST-elevation on ECG on day-1 was -0.89 and decreased to -0.16 on the day of discharge. The average neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NPR) was 0.49, which was high in 144 patients. The mean NLR value was 5.52, indicating a correlation between high NLR values and the magnitude of current injury on admission.
Conclusion: The TANGENTS scoring system can be used as an early evaluation tool for CAD patients with comorbidities to manage and prevent further complications. It allows for progressive differentiation in the severity of clinical outcomes using all the parameters of the score, and the parameters creating the TANGENTS score scale were found to be reliable.
Manorenj, Sandhya; Kumar, S. Sravan; Shashanka, Chillapuram
Anticoagulant initiation after cardioembolic stroke: practical timing and options Journal Article
In: International Journal of Community Medicine and Public Health, vol. 12, iss. 9, pp. 4186-4195, 2025, ISSN: 2394-6032.
@article{Manorenj_2025h,
title = {Anticoagulant initiation after cardioembolic stroke: practical timing and options},
author = {Sandhya Manorenj and S. Sravan Kumar and Chillapuram Shashanka},
url = {https://www.ijcmph.com/index.php/ijcmph/article/view/14185/8653},
doi = {10.18203/2394-6040.ijcmph20252872},
issn = {2394-6032},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-08-30},
urldate = {2025-08-30},
journal = {International Journal of Community Medicine and Public Health},
volume = {12},
issue = {9},
pages = {4186-4195},
abstract = {Cardioembolic Stroke (CES) is a leading cause of Acute Ischemic Stroke (AIS) and is linked to worse outcomes. There is a notably increased risk of “hemorrhagic transformation” (HT) in CES cases, where anticoagulant therapy is essential for patients with atrial fibrillation (AF) to prevent future strokes. Additionally, larger infarcts are associated with a higher risk of HT, effectively doubling the mortality risk. Currently, there are no clear guidelines connecting infarct size to “anticoagulation” decisions or management of HT cases. This review specifically focuses on the timing of “anticoagulation” initiation in patients with AF. Out of 380 articles evaluated, 50 relevant studies were included in this review. Generally, existing guidelines recommend starting “anticoagulation” between 4 to 14 days after anAIS. The review seeks to summarize current research on early versus late “anticoagulation” initiation in AF patients who experience AIS, providing clinicians with practical insights on optimal timing and the selection of effective and safe anticoagulants.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Mirza, Umaid; Shah, Mohammed Nasarullah; Hassan, Khaja Ali; Shakeeb, Mohammed Mukarram Ali
In: Journal of Contemporary Clinical Practice, vol. 11, iss. 8, pp. 935-940, 2025, ISSN: 2457-7200.
@article{Mirza_2025,
title = {Comparative analysis of the efficacy of esmolol 1 mg/kg and dexmedetomidine 0.75 mg/kg in attenuating the hemodynamic pressor response to laryngoscopy and intubation: a prospective randomized study},
author = {Umaid Mirza and Mohammed Nasarullah Shah and Khaja Ali Hassan and Mohammed Mukarram Ali Shakeeb},
url = {https://jccpractice.com/article/comparative-analysis-of-the-efficacy-of-esmolol-1-mg-kg-and-dexmedetomidine-0-75-mg-kg-in-attenuating-the-hemodynamic-pressor-response-to-laryngoscopy-and-intubation-a-prospective-randomized-study-1250/},
doi = {10.61336/jccp/25-08-125},
issn = {2457-7200},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-08-30},
urldate = {2025-08-30},
journal = {Journal of Contemporary Clinical Practice},
volume = {11},
issue = {8},
pages = {935-940},
abstract = {Background: Laryngoscopy and endotracheal intubation provoke significant hemodynamic responses, including hypertension and tachycardia, due to reflex sympathetic stimulation. These responses may lead to complications such as myocardial ischemia and arrhythmias in susceptible patients. Pharmacological agents such as β-blockers and α2-agonists are commonly used to attenuate this pressor response, but their relative efficacy remains a topic of investigation.
Aim: To evaluate and compare the efficacy of Esmolol and Dexmedetomidine in attenuating the hemodynamic pressor response to laryngoscopy and endotracheal intubation and their side effects.
Methods: This prospective randomized study included 80 ASA I–II patients, aged 18–65 years, undergoing elective non-cardiac surgery under general anaesthesia. Patients were randomly assigned to two groups: Group E (Esmolol 1 mg/kg) and Group D (Dexmedetomidine 0.75 μg/kg), administered as infusions 2 minutes prior to induction. Hemodynamic parameters (HR, SAP, DAP, MAP) were recorded at baseline, pre-laryngoscopy, during intubation, and at 1-, 3-, and 5-minutes post-intubation. Statistical analysis was performed using Student’s t-test and paired t-tests, with p<0.05 considered significant.
Results: Dexmedetomidine produced a significantly greater attenuation of HR, SAP, DAP, and MAP compared to Esmolol (p<0.05) during and after intubation. Hemodynamic parameters in Group D returned close to baseline within 5 minutes, while Group E showed sustained elevations. No significant episodes of bradycardia or hypotension were observed in either group.
Conclusion: Dexmedetomidine (0.75 μg/kg) is superior to Esmolol (1 mg/kg) in blunting the hemodynamic response to laryngoscopy and intubation, providing greater cardiovascular stability without significant adverse effects.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Aim: To evaluate and compare the efficacy of Esmolol and Dexmedetomidine in attenuating the hemodynamic pressor response to laryngoscopy and endotracheal intubation and their side effects.
Methods: This prospective randomized study included 80 ASA I–II patients, aged 18–65 years, undergoing elective non-cardiac surgery under general anaesthesia. Patients were randomly assigned to two groups: Group E (Esmolol 1 mg/kg) and Group D (Dexmedetomidine 0.75 μg/kg), administered as infusions 2 minutes prior to induction. Hemodynamic parameters (HR, SAP, DAP, MAP) were recorded at baseline, pre-laryngoscopy, during intubation, and at 1-, 3-, and 5-minutes post-intubation. Statistical analysis was performed using Student’s t-test and paired t-tests, with p<0.05 considered significant.
Results: Dexmedetomidine produced a significantly greater attenuation of HR, SAP, DAP, and MAP compared to Esmolol (p<0.05) during and after intubation. Hemodynamic parameters in Group D returned close to baseline within 5 minutes, while Group E showed sustained elevations. No significant episodes of bradycardia or hypotension were observed in either group.
Conclusion: Dexmedetomidine (0.75 μg/kg) is superior to Esmolol (1 mg/kg) in blunting the hemodynamic response to laryngoscopy and intubation, providing greater cardiovascular stability without significant adverse effects.
Shah, Mohammed Nasarullah; Mirza, Umaid; Hassan, Khaja Ali; Rahman, Shaik Abdul
Segmental epidural anaesthesia for inguinal hernia repair - a clinical study Journal Article
In: European Journal of Cardiovascular Medicine, vol. 15, iss. 8, pp. 893-897, 2025, ISSN: 2042-4884.
@article{Shah_2025,
title = {Segmental epidural anaesthesia for inguinal hernia repair - a clinical study},
author = {Mohammed Nasarullah Shah and Umaid Mirza and Khaja Ali Hassan and Shaik Abdul Rahman},
url = {https://healthcare-bulletin.co.uk/article/segmental-epidural-anaesthesia-for-inguinal-hernia-repair-a-clinical-study-4133/},
doi = {10.61336/ejcm/25-08-162},
issn = {2042-4884},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-08-30},
urldate = {2025-08-30},
journal = {European Journal of Cardiovascular Medicine},
volume = {15},
issue = {8},
pages = {893-897},
abstract = {Background & Objectives: Inguinal hernia repair is among the most common surgical procedures in men worldwide. Epidural anaesthesia is widely utilized, but conventional dosing can lead to hemodynamic instability, particularly in elderly patients. This clinical study evaluated the safety and efficacy of low-dose segmental epidural anaesthesia, targeting only the surgical field to minimize complications.
Methods: A prospective study was conducted on 60 patients (ASA I & II), aged 18–70 years, undergoing elective inguinal hernia repair. Segmental epidural block was performed with 5–6 mL of 0.5% Bupivacaine at the L1–L2 space. The onset, duration, and quality of analgesia were assessed along with pre- and postoperative sensory block levels and hemodynamic parameters (heart rate, systolic and diastolic blood pressure). Adverse effects such as shivering, sweating, bradycardia, and hypotension were also recorded.
Results: The mean onset of analgesia was 7.8 minutes, and the mean duration was 162.25 minutes (range: 120–240 minutes). Analgesic quality was rated as Excellent in 34 patients, Good in 17, Fair in 7, and Poor in 2 cases. Hemodynamic stability was maintained in all patients. Complications were minimal, with shivering observed in 5 cases and sweating in 9.
Conclusion: Segmental epidural anaesthesia using 5–6 mL of 0.5% Bupivacaine provides effective and safe analgesia for inguinal hernia repair, with minimal complications and limited block spread. It is especially advantageous in elderly patients where hemodynamic changes must be minimized.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Methods: A prospective study was conducted on 60 patients (ASA I & II), aged 18–70 years, undergoing elective inguinal hernia repair. Segmental epidural block was performed with 5–6 mL of 0.5% Bupivacaine at the L1–L2 space. The onset, duration, and quality of analgesia were assessed along with pre- and postoperative sensory block levels and hemodynamic parameters (heart rate, systolic and diastolic blood pressure). Adverse effects such as shivering, sweating, bradycardia, and hypotension were also recorded.
Results: The mean onset of analgesia was 7.8 minutes, and the mean duration was 162.25 minutes (range: 120–240 minutes). Analgesic quality was rated as Excellent in 34 patients, Good in 17, Fair in 7, and Poor in 2 cases. Hemodynamic stability was maintained in all patients. Complications were minimal, with shivering observed in 5 cases and sweating in 9.
Conclusion: Segmental epidural anaesthesia using 5–6 mL of 0.5% Bupivacaine provides effective and safe analgesia for inguinal hernia repair, with minimal complications and limited block spread. It is especially advantageous in elderly patients where hemodynamic changes must be minimized.
f) Details of any CME programmes, conferences and/or any academic activities conducted by the institution (Updated 10-08-2023)
g) Details of any awards and achievement received by the students or faculty (Updated 31-07-2024)
MBBS
MD / MS
Teaching staff
Non-teaching staff
h) Details of the affiliated university and its Vice-Chancellor and Registrar (Updated 26-07-2024)
Kaloji Narayana Rao University of Health Sciences
Address: Nizampura, Warangal-506007, Telangana, India.
Phone: 0870 2454555
Email: knruhswgl15@gmail.com
Dr. P. V. Nanda Kumar Reddy
Designation: Vice-Chancellor
Phone: 0870 2454555 (Ext. 101)
Email: knruhswgl15@gmail.com
Dr. S. Sandhya
Designation: Registrar
Phone: 0870 2454555 (Ext. 103)
Email: reg-wgl-knruhs@telangana.gov.in
i) Result of all the examinations of last one year (Updated 10-08-2023)
| Batch | Year 2021 | Year 2022 | Year 2023 | |||||||||
| I MBBS | Regular | Supplementary | Regular | Supplementary | Regular | Supplementary | ||||||
| No. | % | No. | % | No. | % | No. | % | No. | % | No. | % | |
| Candidates appeared | 150 | 54 | 150 | 59 | 150 | 21 | ||||||
| Candidates passed | 105 | 70% | 40 | 74% | 110 | 73% | 30 | 51% | 123 | 82% | 13 | 62% |
| Batch | Year 2021 | Year 2022 | Year 2023 | |||||||||
| II MBBS | Regular | Supplementary | Regular | Supplementary | Regular | Supplementary | ||||||
| No. | % | No. | % | No. | % | No. | % | No. | % | No. | % | |
| Candidates appeared | 146 | 2 | 144 | 21 | 137 | 9 | ||||||
| Candidates passed | 131 | 90% | 1 | 50% | 109 | 76% | 17 | 81% | 114 | 83% | 4 | 44% |
| Batch | Year 2021 | Year 2022 | Year 2023 | |||||||||
| Final MBBS – Part I | Regular | Supplementary | Regular | Supplementary | Regular | Supplementary | ||||||
| No. | % | No. | % | No. | % | No. | % | No. | % | No. | % | |
| Candidates appeared | 147 | 21 | 146 | 12 | 132 | 8 | ||||||
| Candidates passed | 129 | 88% | 18 | 86% | 130 | 89% | 9 | 75% | 99 | 75% | 5 | 63% |
| Batch | Year 2021 | Year 2022 | Year 2023 | |||||||||
| Final MBBS – Part II | Regular | Supplementary | Regular | Supplementary | Regular | Supplementary | ||||||
| No. | % | No. | % | No. | % | No. | % | No. | % | No. | % | |
| Candidates appeared | 148 | 3 | 145 | 24 | 135 | 2 | ||||||
| Candidates passed | 142 | 96% | 2 | 67% | 139 | 96% | 10 | 42% | 131 | 97% | 2 | 100% |
MD / MS
DM / MCh
j) Detailed status of recognition of all the courses (Updated 10-08-2023)
k) Details of clinical material in the hospital (Updated 10-08-2023)
| In the entire hospital (Calendar Year 2022) | |
| OPD | 609375 |
| IPD (Total Number of Patients admitted) | 60101 |
| Deaths | 847 |
l) Measures undertaken to curb the menace of ragging in terms of Prevention and Prohibition of Ragging in Medical Colleges/Institutions Regulations, 2021 (Updated 10-08-2023)